Matthew Regis
Benchmarking is an important aspect of software development, as it allows you to measure the performance of your code and identify any potential bottlenecks or areas for improvement. In the .NET ecosystem, the BenchmarkDotNet library is a popular tool that makes it easy to create and run benchmarks.
To get started with BenchmarkDotNet, you first need to install the library using the following command:
dotnet add package BenchmarkDotNet
Once the library is installed, you can create a benchmark by creating a new class and decorating it with the [Benchmark] attribute. Inside this class, you can define one or more methods that you want to benchmark, and decorate each method with the [Benchmark] attribute. For example, the following code defines a simple benchmark that measures the performance of the string.Concat method:
using System;
using System.Text;
using BenchmarkDotNet.Attributes;
public class StringConcatBenchmark
{
[Benchmark]
public string Concat()
{
return string.Concat("Hello ", "World");
}
}
To run this benchmark, you can use the dotnet run command, and BenchmarkDotNet will automatically run the benchmark and display the results. The results will include the time it took to run each method, as well as the number of operations per second that the method was able to perform.
In addition to measuring the performance of individual methods, BenchmarkDotNet also allows you to compare the performance of different implementations of the same algorithm. For example, the following code defines two different implementations of a string concatenation algorithm, and uses BenchmarkDotNet to compare their performance:
using System;
using System.Text;
using BenchmarkDotNet.Attributes;
public class StringConcatBenchmark
{
private const int N = 10000;
[Benchmark]
public string Concat()
{
var sb = new StringBuilder();
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
sb.Append("Hello ");
sb.Append("World");
}
return sb.ToString();
}
[Benchmark]
public string Interpolation()
{
var sb = new StringBuilder();
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
sb.Append($"Hello {i}");
}
return sb.ToString();
}
}
When you run this benchmark, BenchmarkDotNet will run both methods and compare their performance. This can help you determine which implementation is faster, and can guide your decision about which implementation to use in your application.
The easiest way to run benchmark is to put it in a console app. For the example code above you would add the following code to the console app, usually in the program.cs file.
using BenchmarkDotNet.Running;
BenchmarkRunner.Run<StringConcatBenchmark>();
When running benchmarks, it should be done in Release mode for obvious reasons. The easiest way to run it in my opinion, is goto the location of the csproj file of your console app in your terminal and run the dotnet run command in release configuration, like so:
dotnet run --configuration Release
The source code to this example can be found here
If run correctly you should get an output like the image below:
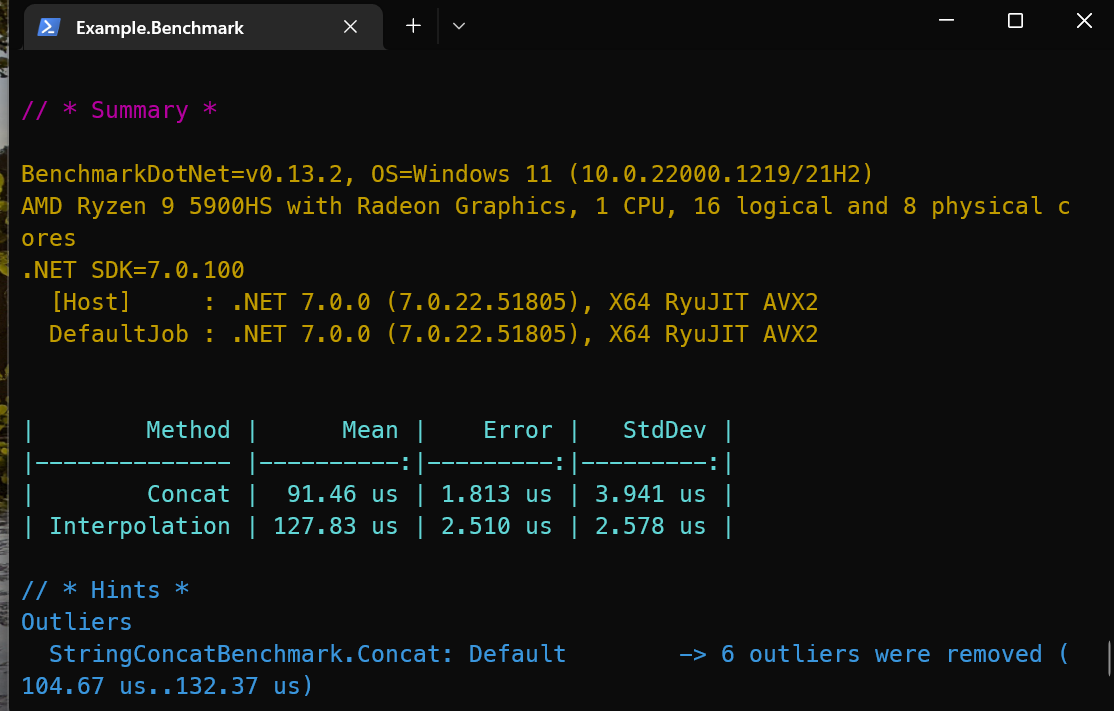
Overall, BenchmarkDotNet is a powerful and easy-to-use tool for measuring the performance of your .NET code. Whether you are working on a small personal project or a large enterprise application, BenchmarkDotNet can help you ensure that your code is running as efficiently as possible.